In this lesson, you will learn everything about irregular verbs in the German language. Gain a deep understanding of how they function, how their forms change, and how to use them in different contexts (at different times). You will also have access to a list of irregular verbs along with their translations.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!CONTENTS
What are strong ’irregular’ German verbs?
The Present Tense
The Past Tense
The Perfect Tense
What are strong ’irregular’ German verbs?
The Present Tense
Strong verbs are able to change their stem in certain forms. Originally, these stem changes occurred to make some verb forms easier to pronounce. Not many verbs change their stem in the Present Tense; they only change in the du and er/sie/es forms. The other ‘persons’ are not affected by stem changes.
Here you can see the lists of irregular verbs:
List of irregular verbs A1
List of irregular verbs A2
List of irregular verbs B1
List of irregular verbs B2
These changes, which can make learning challenging, are also known as irregular verbs. Here are some of the most important ones.
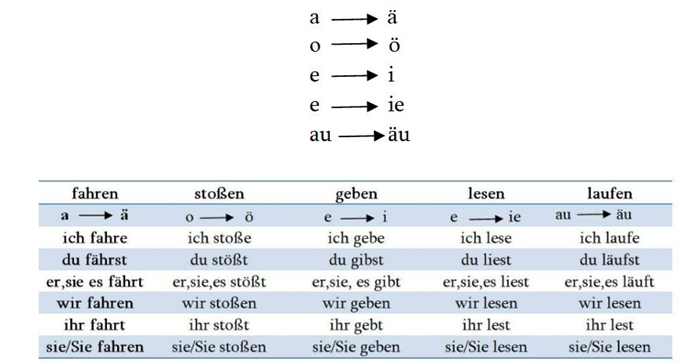
Changes from:
a – ä
o – ö
e – i
e – ie
au – äu
| -e- to -i- | ich gebe, du gibst, er,sie,es gibt ich spreche,du sprichst, er,sie,es spricht |
| -e- to -ie- | ich lese, du liest, er,sie,es liest ich sehe, du siest, er,sie,es sieht |
| -a- to -ä- | ich fahre, du fährst, er,sie,es fährt ich fange, du fängst, er,sie,es fängt |
| geben | sprechen | lesen | sehen | fahren | fangen |
| ich gebe du gibst er,sie,es gibt wir geben ihr gebt sie geben | ich spreche du sprichst er,sie,es spricht wir sprechen ihr sprecht sie sprechen | ich lese du liest er,sie,es liest wir lesen ihr lest sie lesen | ich sehe du siehst er,sie,es sieht wir sehen ihr seht sie sehen | ich fahre du fährst er,sie,es fährt wir fahren ihr fahrt sie fahren | ich fange du fängst er,sie,es fängt wir fangen ihr fangt sie fangen |
The Past Tense
This is where things start to get a little tricky, but don’t worry, it’s totally conquerable☺🏄♀️🤸♂️💪. The key is to remember the irregular verbs in the past tense. The infinitive stem changes and we add the following suffixes to that changed stem: -, -st, -, -en, -t, -en.
Here is an example of the verb gehen in the past tense:
ich ging
du gingst
er,sie,es ging
wir gingen
ihr gingt
sie/Sie gingen
As you can see the first and third person singular has NO suffix, and the verb is pronounced exactly the same in the first and third person both singular and plural.
Click on:
Grammar Content
The Perfect tense
The changes that occur in the past perfect tense have already been explained in the lesson Participles I and II in the German Language.
Participle II of irregular verbs in the German language is built by adding the prefix ge- and the suffix -en to the variable stem:
ge- + variable stem + –en
Since it is recommended to learn these verbs by heart, I have listed them for you above.
See more:



