In this lesson, you will learn all about coordinating conjunctions in German, known as “Konjunktionen.” I will provide a list of all the coordinating conjunctions, along with their meanings, how and when they are used, the position of the verb in sentences, and examples of sentences that are introduced by coordinating conjunctions.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!CONTENTS
What are coordinating conjunctions?
Connecting main clauses
The most common coordinating conjunctions
Connecting dependent clauses
Connecting the parts of the clause
What are coordinating conjunctions?
Coordinating conjunctions connect main clauses, parts of the clause and dependent clauses that depend on the same main clause.
For example:
Wir gehen morgen schwimmen, außer es regnet. – We’re going swimming tomorrow, unless it rains.
Es schneit, aber es ist nicht kalt. – It’s snowing, but it’s not cold.
Sie versuchte zu bremsen, doch es war zu spät. – She tried to brake, but it was too late.
Er fuhr schneller und schneller. – He drove faster and faster.
The following are the coordinating CONJUNCTIONS in German.
aber (but), allein (however, but), außer (exept), denn (because), doch (but, but still), jedoch (however), oder (or), sondern (but), sowie (as well as), und (and)
Connecting main clauses
If the main clauses are connected by coordinating conjunctions, then their word order does not change. The verb is placed second in the sentence, and the second part of the predicate is placed at the end of the sentence.
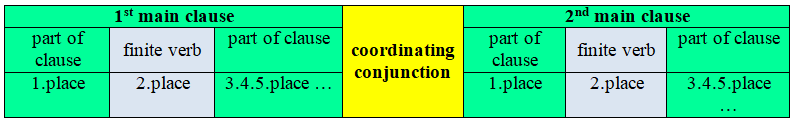
The most common coordinating conjunctions

In this table, the verbs are in bold to make it easier to see where the verbs are in the sentence.
Click on:
Grammar Contents
Connecting dependent clauses
Coordinating conjunctions can only connect dependent clauses of the same degree, i.e. dependent clauses that depend on the same main clause.

As you can see in the table above, an independent conjunction connects two dependent clauses, which depend on the main clause. However, the order of words in dependent clauses is according to the rule for dependent clauses, that is, the verbs are at the end of the sentence.
Connecting the parts of the clause
All coordinating conjunctions except denn connect parts of sentences.
Examles:
subjecte + subjecte: Sie ist Frau und Mutter.
object + object: Es gibt nur Sieger oder Verlierer.
adverb + adverb: Wir fahren dieses Jahres an die Adria bzw. auf die Insel Krk.
See more:
